tudor ribozyme | tudor methylation protein tudor ribozyme We report the discovery and analysis of an additional self-cleaving ribozyme class, called twister, which is present in many species of bacteria and eukarya. After announcing the update of the Calibre 1861 in 2019 with the Co-Axial Master Chronometer Calibre 3861, we were all anxiously waiting to see how Omega was .
0 · tudor methylation protein
1 · tudor methylation function
2 · tudor germ cells
3 · tudor gene
Oyster, 41 mm, Oystersteel. Oyster architecture. Monobloc middle case, screw-down case back and winding crown. Diameter. 41 mm. Material. Oystersteel. Bezel. Unidirectional rotatable 60-minute graduated, scratch-resistant Cerachrom insert in black ceramic, numerals and graduations coated in platinum. Winding crown. Screw-down, Triplock .
A strong case can be made that mtrRNA is needed for germ cell formation, as ribozyme-mediated depletion of mtlrRNA results in a severe reduction of the number of pole cells formed 69.
A genome-wide screen discovers a naturally occurring ribozyme in humans termed hovlinc, which is embedded within a long noncoding RNA and has no apparent relation to .
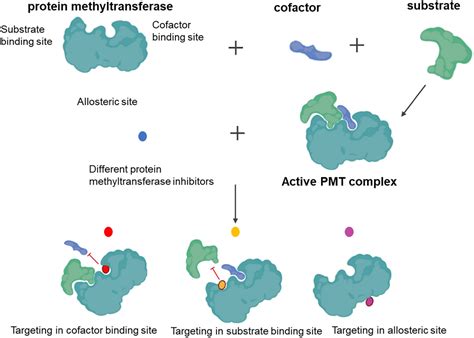
The Tudor domain comprises a family of motifs that mediate protein–protein interactions required for various DNA-templated biological processes. Emerging evidence .
Here, we discuss novel functions of a number of Tudor-containing proteins (including JMJD2A, 53BP1, SGF29, Spindlin1, UHRF1, PHF1, PHF19 and SHH1) in ‘reading’ unique methylation .
We report the discovery and analysis of an additional self-cleaving ribozyme class, called twister, which is present in many species of bacteria and eukarya.
Small endonucleolytic ribozymes promote the self-cleavage of their own phosphodiester backbone at a specific linkage. The structures of and the reactions catalysed .We first present an overview of ribozymes, riboswitches and other related RNA sensors, and highlight their impact on gene regulation. We then analyse their structure–function . McRae, Wan, Kristoffersen et al. recently revealed how these RNA replicases might have functioned by solving the structure of an artificial polymerase ribozyme. This work . The term ribozyme is used for RNA that can act as an enzyme. Ribozymes are mainly found in selected viruses, bacteria, plant organelles, and lower eukaryotes. Ribozymes .
The research team tested the activity of over 2,600 different RNA sequences predicted to belong to a class of RNA enzymes called "twister ribozymes," which have the .This volume provides protocols designed to study the function and the structure of diverse ribozymes. Chapters guide readers through different techniques to identify and characterize new ribozymes and methods to use ribozymes to alter the function of CRISPR-based guide RNAs, AgoshRNAs and aptamers or to study RNA capping and long non-coding RNAs. The ωRNA construct was designed with a hepatitis delta virus self-cleaving ribozyme at the 3′ end to produce a fixed-length 21-nt guide RNA (gRNA) 12,13.
Ribozyme RNA is heated at 50 °C for 5 min in the reaction buffer, incubated at 37 °C for 2 min, and then added into the preheated substrate RNA. 3. HEK 293 cells are cultured with 80 % confluency before infection. The cells come apart 2–3 days post infection depending on the concentration of adenoviral vectors. Sometimes, cells become so . Cloning and expression of ribozyme in HeLa cells. We constructed the hammerhead ribozyme targeting the pseudoknot region of human telomerase RNA at GUC corresponding to 180th nucleotide on hTR (Fig. 1A).Expression cassettes for the active and mutant ribozyme were constructed by inserting these sequences in a mammalian expression . Ribozyme – RNA that acts as a biological catalyst, which in a ribosome helps form peptide bonds. Ribosomal RNA – RNA molecules associated with ribosomes, some of which are ribozymes and catalyze reactions. Ribonucleic Acid – Otherwise known as RNA, this molecule usually exists as a single-stranded carrier of genetic information. The ribozyme appears to be functional in vivo and is embedded within a long noncoding RNA belonging to a class of very long intergenic noncoding RNAs. The presence of a catalytic RNA enzyme in .
Ribozymes are RNA molecules that act as chemical catalysts, a shortening of ribonucleic acid enzymes.In the contemporary biosphere, the known ribozymes carry out a relatively limited range of reactions (), mostly involving phosphoryl transfer, notably transesterification (the large majority) and hydrolysis reactions.However, the discovery that .
wholesale rolex dhgate
However, the identification of the bacterial ribozyme glmS, which specifically binds a metabolite and cleaves the mRNA encoding the protein that controls the metabolism of that metabolite, has established a closer link between riboswitches and ribozymes 7. Recent findings of novel riboswitches, ribozymes and other RNA-based regulatory elements .
Ribozyme library design and analysis. (a) Secondary structures of F1* and 4d394 ligase ribozymes with cognate substrates.Catalytic cores are shown in red. (b) Ribozyme library Lib-N7/8.Nucleotides . The ribozyme assumes an elongated hairpin-like architecture preorganized to accommodate the epoxide substrate in a hook-shaped conformation. Observed reactivity of substrate analogs together with .
tudor methylation protein
One such gene is tudor (tud); without proper tud function germ cell formation does not occur. . as ribozyme-mediated depletion of mtlrRNA results in a severe reduction of the number of pole . The tetrahymena ribozyme Cech’s team discovered was an intron itself and evidence has since demonstrated that as well as having intrinsic catalytic activity, some introns code for proteins that . Please use one of the following formats to cite this article in your essay, paper or report: APA. Robertson, Sally. (2023, July 20). Ribozyme Discovery.
Ribozyme. The well-established natural ribozymes are the hammerhead, hairpin, hepatitis delta virus (HDV), Varkud Satellite (VS), GlmS, twister, twister sister, pistol and hatchet ribozyme, which make up the category of small ribozymes, as well as the group I and II introns, the ribosome, spliceosome and RNase P, which are classified as large ribozymes (Discovery . A strong case can be made that mtrRNA is needed for germ cell formation, as ribozyme-mediated depletion of mtlrRNA results in a severe reduction of the number of pole cells formed 69. A genome-wide screen discovers a naturally occurring ribozyme in humans termed hovlinc, which is embedded within a long noncoding RNA and has no apparent relation to known ribozymes. The Tudor domain comprises a family of motifs that mediate protein–protein interactions required for various DNA-templated biological processes. Emerging evidence demonstrates a versatility of the Tudor family domains by identifying their specific interactions to a wide variety of histone methylation marks.
Here, we discuss novel functions of a number of Tudor-containing proteins (including JMJD2A, 53BP1, SGF29, Spindlin1, UHRF1, PHF1, PHF19 and SHH1) in ‘reading’ unique methylation events on histones in order to facilitate DNA damage repair or regulate transcription. We report the discovery and analysis of an additional self-cleaving ribozyme class, called twister, which is present in many species of bacteria and eukarya. Small endonucleolytic ribozymes promote the self-cleavage of their own phosphodiester backbone at a specific linkage. The structures of and the reactions catalysed by members of individual families have been studied in great detail in the past decades.
We first present an overview of ribozymes, riboswitches and other related RNA sensors, and highlight their impact on gene regulation. We then analyse their structure–function relationships, dissecting the features that are essential for gene expression control and other cellular processes. McRae, Wan, Kristoffersen et al. recently revealed how these RNA replicases might have functioned by solving the structure of an artificial polymerase ribozyme. This work illustrates how complex RNA structures evolve, with implications for the origins of life. The term ribozyme is used for RNA that can act as an enzyme. Ribozymes are mainly found in selected viruses, bacteria, plant organelles, and lower eukaryotes. Ribozymes were first discovered in 1982 when Tom Cech’s laboratory observed .
tudor methylation function
tudor germ cells
$11K+
tudor ribozyme|tudor methylation protein